Note: Information provided on this page is for general education only, please seek medical assistance when in doubt
The embryonic period in humans begins at fertilization when the male sperm cell penetrates into woman’s egg and this period continues until the end of 10th week of gestation. The period of two weeks from fertilization is also referred to as the germinal stage.
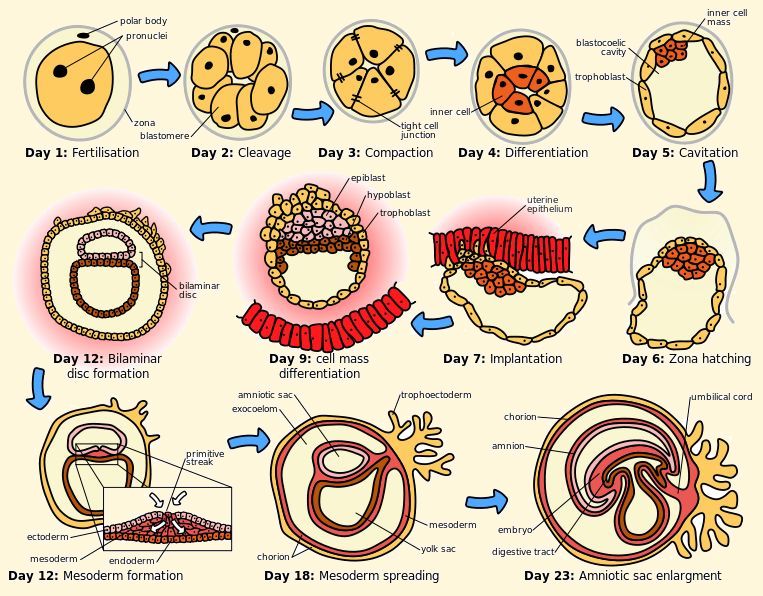
Starting out as a single cell zygote, the embryo spends next few days traveling down the Fallopian tube and then divides several times to form a ball of cells called a morula. Further cellular division is accompanied by the formation of a small cavity between the cells. This stage is called a blastocyst.
Till this point there is no growth in the overall size of the embryo, as it is confined within a glycoprotein shell, instead, each division produces successively smaller cells.
Blastocyst reaches the uterus at roughly the fifth day after fertilization. It is here that lysis of the zona pellucida occurs. This process is analogous to zona hatching, a term that refers to the emergence of the blastocyst from the zona pellucida, when incubated in vitro.
This allows the trophectoderm cells of the blastocyst to come into contact with, and adhere to, the endometrial cells of the uterus. The trophectoderm will eventually give rise to extra-embryonic structures, such as the placenta and the membranes.
The embryo becomes embedded in the endometrium in a process called implantation. In most successful pregnancies, the embryo implants 8 to 10 days after ovulation. The embryo, the extra-embryonic membranes, and the placenta are collectively referred to as a conceptus, or the "products of conception".
Rapid growth occurs and the embryo's main external features begin to take form. This process is called differentiation, which produces the varied cell types such as blood cells, kidney cells, and nerve cells.
In first 10 weeks of gestation the cell divides rapidly and begin to differentiate into the various body systems, the basic outlines of the organ, body, and nervous systems are established. By the end of the embryonic stage, the beginnings of features such as fingers, eyes, mouth, and ears become visible, during this time, there is also development of structures important to support the embryo, including the placenta and umbilical cord.
Placenta connects the developing embryo to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply while the umbilical cord is the connecting cord from the embryo or fetus to the placenta.
Pregnancy Trimesters
» First Trimester
» Second Trimester
» Third Trimester
| Fetal Growth in ... | |||
| 1st month | 2nd month | 3rd month | 4th month |
| 5th month | 6th month | 7th month | 8th month |
| 9th month | 10th month | ||





